
A Guide To Repairing Family Relationships
Discover expert tips for repairing family relationships and fostering healthy connections with The Recovery Team.
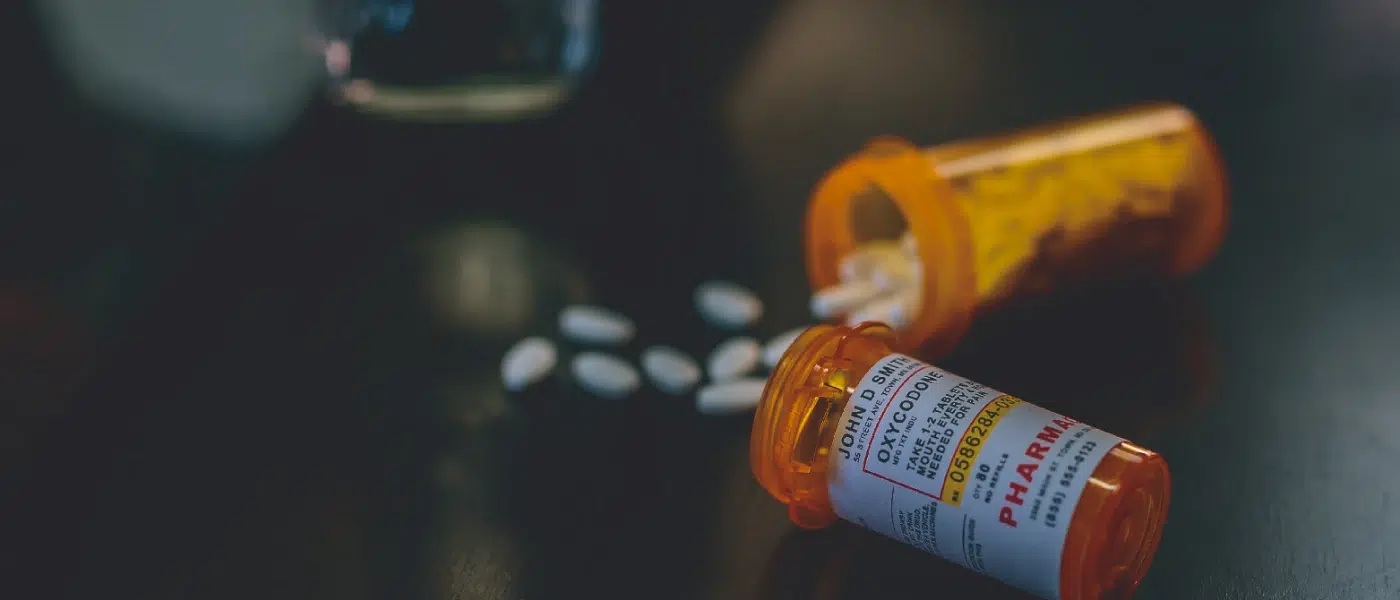
Opioid addiction is common among Americans due, in part, to the Ove prescription of opioid pain relievers. Moreover, opioid abuse leads to opioid use disorder, and more than 2.5 million Americans have faced the condition of opioid use disorder.
Opioid use disorder contributed to more than 28,000 overdose deaths in 2014.
Those who are going through opioid use disorder need opioid rehab. The rehab process makes you recover from opioid use disorder. Rehab centers, like The Recovery Team, offer this treatment.
Opioid addiction alters the functioning of the brain; that’s why the addiction has a long-lasting impact on the individual. Participants in opioid treatment programs need to learn new skills to prevent relapse and handle any additional problems, such as mental health diseases.
Opioid addiction treatment is done with several methods, such as:
Seek help from The Recovery Team today for opioid treatment by contacting us at (800) 817-1247.
Opioid use disorder or opioid addiction is a chronic medical condition that has a long-lasting impact on the brain and other parts of the body.
Medical professionals recommend that for the diagnosis of an opioid use disorder, you must have two symptoms which are listed below:
Treatment is necessary to overcome opioid addiction, as long-term dependence on drugs causes physical and mental health issues.
If a person sees signs of opioid overdose or addiction, they should immediately consult medical professionals. The doctors can recommend the right procedure for treating opioid use disorder.
The recovery process starts with the treatment of any drug overdoses. There are different treatment options that your healthcare provider suggests to you. Moreover, patients with chronic pain need primary care.
If your loved one needs help regarding opioid treatment, then you should find a physician or health care professional first. They will recommend you some experts in the field of addiction medicine.
Reassure your loved one that opioid addiction can be effectively managed, but it can take multiple therapy efforts before the right strategy is found.
Engaging in an aggressive “intervention” is not advised if your friend or loved one refuses to ask for assistance. These interactions may turn violent or have other unintended consequences. Make an effort to persuade the person to see a doctor.
Opioid use leads to the development of opioid addiction in users. Opioids are highly addictive, in large part because they activate the powerful reward centers of your brain.
Endorphins, the brain’s feel-good neurotransmitters, are released in reaction to opioid consumption. Endorphins reduce pain perception and increase pleasure, resulting in a brief but powerful feeling of well-being.
After an opiate dose wears off, you can find yourself longing for those good feelings to return as soon as possible. The initial step toward a potential addiction is being taken here.
Some of the causes of opioid addiction are:
It seems that those who have addicted family members are more likely to become addicted themselves. Genetic traits are one component when discussing the risks of opioid addiction.
Still, other factors such as environment, lifestyle, and other non-genetic characteristics that family members share may also play a role in this elevated risk.
Although many affected people have a family history of opioid or other substance addiction, there is no clear inheritance pattern for opioid addiction.
Even when the drugs are properly prescribed and taken as prescribed, some people still have a significant risk of developing an addiction to opioids. Prescription opioids are frequently mishandled or given to others.
The individuals facing addiction may put procuring and using these drugs before other responsibilities, which frequently severely impacts their interpersonal and professional connections.
It’s unclear why certain people are more prone to addiction than others. Because opioids alter brain chemistry and cause drug tolerance, a higher dose must eventually be used to produce the same results.
Opioid addiction causes serious health impacts on your life which may lead to death if left untreated.
Opioids are most addictive when taken in ways other than prescribed, like being injected or snorted.
Another factor is how long you use prescription opioids. According to research, using opioid drugs for a prolonged time raises the likelihood that you will become addicted to them.
After just five days on opioids, there is a greater chance that you will still be using them a year after beginning a short course.
Addiction can develop quickly or over a long period of opioid usage, and several additional factors, including psychological, genetic, and environmental influences, might contribute.
Some of the risk factors are mentioned below:
The availability of the substance is one of the risk factors for the development of opioid addiction in an individual. Opioid misuse has become common due to the excessive use of this drug. Opioids are often prescribed after surgery.
When the drug is available, there is an increased risk of overdose. In the United States, there are approximately 28,000 individuals who lost their lives due to opioid overdose.
Opioids have a high potential to cause addiction in individuals. When a person uses it daily, then they become dependent on it. Drug availability at home or anywhere is a risk factor for drug dependence.
Association with peers who abuse opioids, fame, bullying, and gang membership are social risk factors.
Peer pressure forces a person to consume drugs. Sometimes just for pleasure, people at a young age have opioid misuse.
Teenagers, in particular, can easily develop an addiction to opioids due to their less developed prefrontal cortex, making them more susceptible to peer pressure. That’s why social pressure is one of the leading risk factors for developing opioid addiction.
Suppose an individual does not have a clear and sober support system. In that case, they may begin or continue to use and abuse opioids.
If someone is addicted in the family, they hesitate to take support from family, as no one helps. This results in relapse, even if they want to recover from addiction.
Opioids, when consumed improperly, cause side effects and risks. These risks are not limited to your health, safety, relationships, and employment.
Some of the effects are mentioned below:
When an individual develops tolerance to a drug, then they want to consume more of the drug. In the case of opioids, it has a high addiction potential. That’s why an individual wants to take it repeatedly.
If you consume opioid regularly, then it becomes a threat to you while driving. Your safety is at risk in these situations. Misusing opioids increases the risk of dangerous behavior, such as driving under the influence and overdose deaths.
People who are addicted to drugs will often lie to hide their addiction from their family and friends. Losing trust is the inevitable outcome of persistent lying.
Family members of people with drug problems may experience betrayal, bitterness, and a loss of respect. The more someone battles addiction, the worse these feelings become until the relationship breaks down. Once lost, trust is difficult to recover.
It’s time to get assistance if you or a loved one has an opioid addiction that is destroying your relationships and life.
The excessive use of opioids leads to opioid addiction. As addiction is an obsession, employees may no longer focus on their work but instead on obtaining the drug.
Opioid addiction diverts an employee’s focus, and they face difficulty focusing on their work. Opioid use might be a safety issue in certain professions. These professions often include frequent drug testing, which would be impossible to pass while addicted to opioids.
The working potential of an employee is also reduced while having an addiction.
Opioids can have negative side effects such as constipation, nausea, drowsiness, and mental fog. They might also slow respiration, which increases the risk of overdose fatalities.
Using prescribed opioids carries additional hazards, such as dependence and addiction. Dependency refers to experiencing withdrawal symptoms after stopping a drug.
A person with an addiction compulsively seeks out substances even though doing so is harmful. Addiction is a chronic brain disorder. If you misuse the medications, your chances of developing dependence and addiction are higher.
Rehab centers offer complete treatment programs for opioid addiction and opioid use disorder (OUD). Rehabilitation centers have experienced healthcare professionals who will look after you.
The treatment of opioid addiction varies from one individual to another. Medication and medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction are both evidence-based methods of treatment.
A treatment program that involves opioid addiction medicine boosts the likelihood of success.
The treatment for OUD usually begins with a medical detox. Detox is the procedure by which drugs and other addictive substances are cleared from your body.
Detox is a painful process, and patients experience withdrawal symptoms after detox. There are certain medications to ease the withdrawal symptoms. The detox takes place at the rehab center under medical supervision.
A patient undergoing medically supervised opioid withdrawal, commonly referred to as detoxification, receives medicine to lessen the severity of withdrawal symptoms that develop when they stop taking opioids.
The main goal of supervised withdrawal is to successfully and securely transition the patient to opioid use disorder medication.
Medication-assisted therapy (MAT) or a medically supervised detox is the usual first step in opioid use disorder rehab. Following that, each person will start a customized addiction treatment program.
Consider the advantages of both treatment choices when considering whether outpatient rehab or inpatient rehab is the best course of action. Residential rehab or inpatient treatment is recommended for severe opioid addiction.
Residential rehab includes behavioral therapies which help a patient in recovering from addiction. An outpatient rehab follows the inpatient treatment to recover and regain sobriety.
Behavioral therapy is a crucial part of opioid addiction treatment in these programs. The following are a few of the therapeutic modalities we use in our substance misuse treatment programs:
Whether a person attends individual or group therapy, behavioral therapy can have a profoundly positive impact on their lives.
People can talk about their struggles in therapy with therapists and addiction specialists who have firsthand experience coping with addiction.
Additionally, in group therapy, patients can share their challenges and triumphs with other people in recovery.

Discover expert tips for repairing family relationships and fostering healthy connections with The Recovery Team.

Discover practical tips on how to set boundaries with people in this expert guide from The Recovery Team.
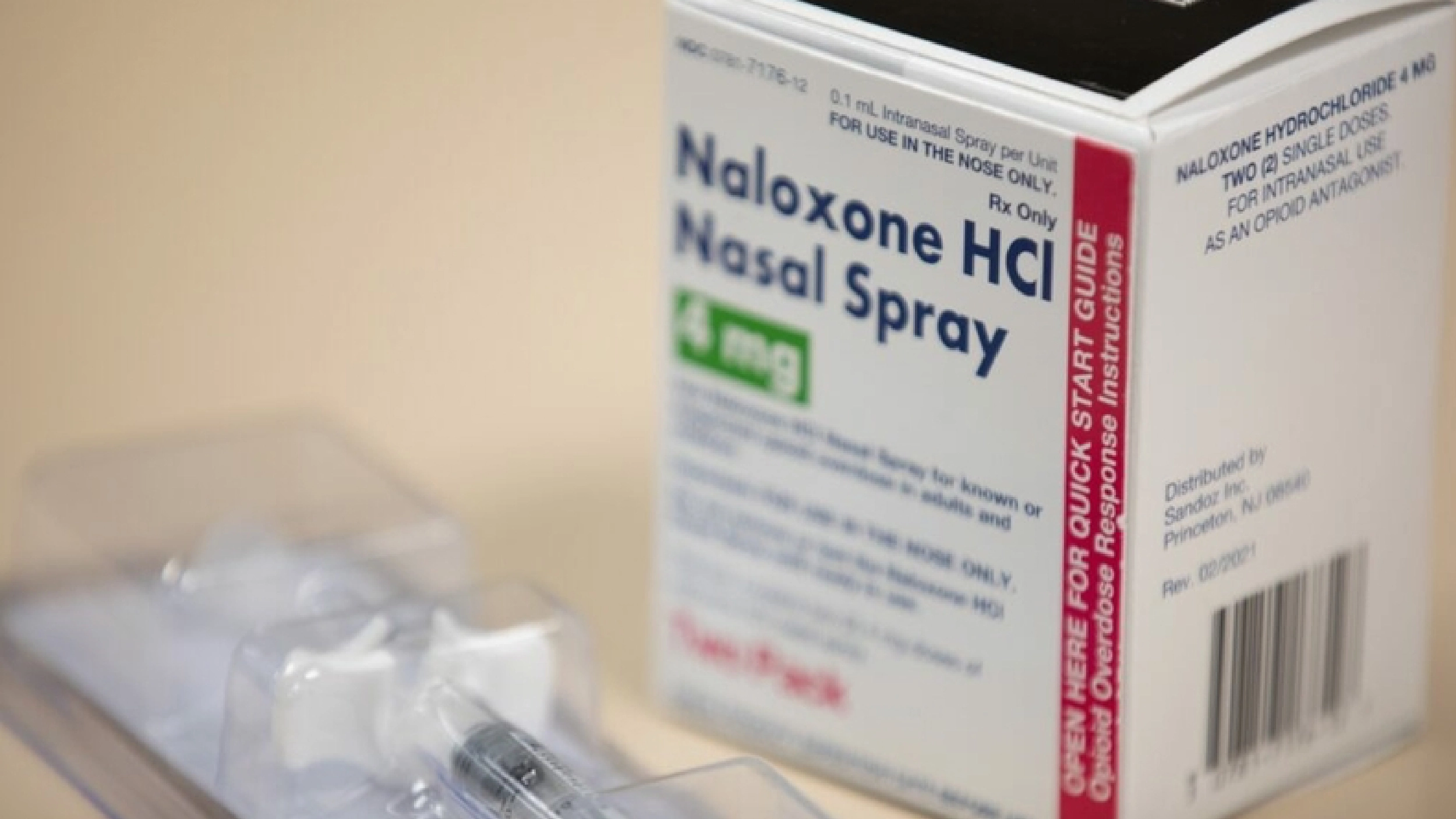
Naloxone saves lives. The Recovery Team shares how to reverse an opioid overdose with this drug.
We advise medical management as the first line of treatment for most people with moderate to severe opioid use disorder (OUD). Additionally, adding psychological therapy is advised.
Clinical trials and investigations have demonstrated that OUD medicine supports sobriety, enhances treatment adherence, and is linked to a decrease in mortality throughout treatment periods. These statistics are covered in depth elsewhere.
Typically, doctors choose an opioid agonist (methadone or buprenorphine) over an opioid antagonist to first treat moderate to severe OUD (i.e., naltrexone). Naltrexone is an approved medication by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
There are multiple ways to stop consuming opioids so that it does not lead to opioid abuse. These ways include: